The hip absorbs great stresses and forces as it bears weight while we are standing and walking. As a result, hip pain is common in structures including the joint and muscles surrounding the hip, ligaments or the hip capsule or labrum. More than 63,000 hip replacements were performed in Canada in 2019–2020.[i] Hip replacement rehabilitation in both the pre and post operative phases has been shown to improve patient outcomes.
The hip is a complex joint. Maintaining its health and stability can lead to increased function and decreased pain in the long term. In this article we will look at how the hip functions, how you can keep this joint healthy and what’s involved in hip replacement surgery and rehabilitation.
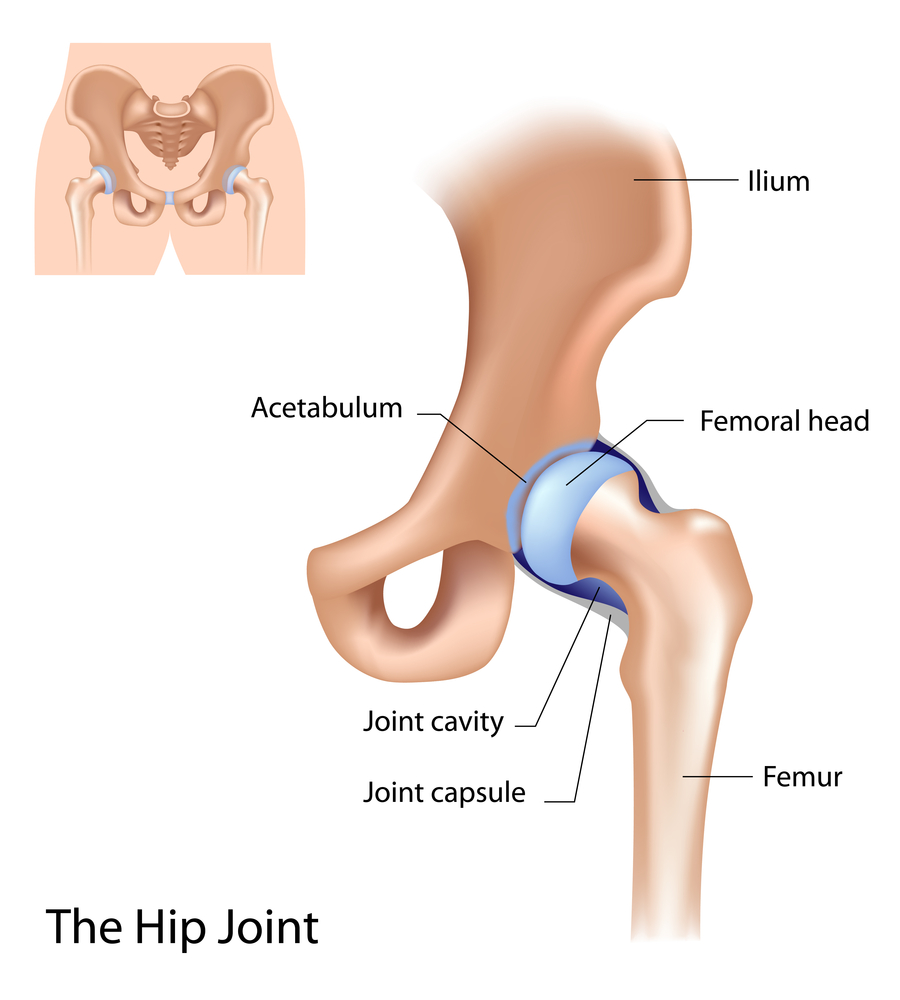
Hip Anatomy
The hip is a ball and socket joint. It is the largest weight bearing joint of the body. When the joint is healthy, the head of the femur (thighbone) forms a round ball that fits into the acetabulum, a cavity at the base of the pelvis that forms the socket.
Hip Joint Function
The hip joint connects the lower extremities to the axial skeleton. The hip joint allows for movement in three major planes. This contributes to stability of the joint and allows for weight bearing of the leg. The primary function of the hip joint is to provide dynamic support to the weight of the body. At the same time, it helps with force and load transmission from the skeleton to the lower extremities. This allows for mobility.[ii]
Healthy Hips Strategies
Healthy hips are important for pain free sitting, walking, and running. Injury and pain in the hip joints can severely impact everyday function. Here are some tips for keeping your hips healthy:
- Ensure strengthening and flexibility of hip muscles as a component of your exercise routine
- Maintain a healthy body weight to avoid extra stress and force through the hip joint
- Take steps to minimize risk of falls (e.g., ensure proper footwear, clear pathways from clutter)
- Listen to your body and seek help if you are injured or pain persists
Common Causes of Hip Pain
Hip pain can be due to a wide variety of causes and structures including the joint, muscles surrounding the hip, ligaments or the hip capsule or labrum. A thorough history and examination will help to determine the cause of pain.
The location of hip pain is important in determining potential causes. Hip pain is often divided into anterior, lateral or posterior pain. Common causes in these areas are:
Anterior – osteoarthritis, labral tears, iliopsoas bursitis or strain, hernia
Lateral – trochanteric bursitis, iliotibial band syndrome, gluteus medius tear
Posterior – piriformis syndrome, sacroiliac joint dysfunction, referred pain from the lumbar spine
Hip Problems That Might Require Surgery
When the cause of hip pain is intra articular (within the joint), surgery may be warranted. Surgery can either be done through arthroscopy (minimally evasive approach) or open surgery (involving large incision).
Arthroscopic hip procedures can involve debridement (removal of loose or damaged tissue), repair of a labral tear, or for treatment of hip impingement.
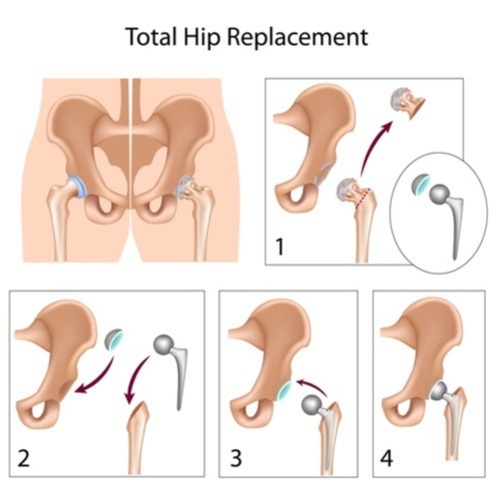
The most common need for open surgery of the hip is for a total hip replacement. A hip replacement addresses the pain, stiffness and decreased function that often results due to advanced arthritis or other diseases causing significant hip joint damage.
Hip Replacement Surgery
More than one million hip replacement operations are performed every year worldwide and this is anticipated to double within the next decade.[iii] Fortunately, total hip replacements are one of the most successful operations performed worldwide.[iv]
There are various techniques, material and designs used in hip replacement surgery that depend on the client presentation. All surgeries consist of a ball component (made of strong metal or ceramic material) and the socket component (made of plastic, ceramic or metal).[v] These prosthetic materials are pressed into the bone (to allow the bone to grow over the component) or cemented in. The surgeon removes the damaged cartilage and bone and then positions new implants to restore the alignment and function of your hip.[vi]
Hip Replacement Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation has been found to be an integral component in both the pre and post operative phases of hip replacement rehabilitation.[vii] This rehabilitation consists of multiple components:
- Education – Both pre- and post- operative education is crucial in providing clients with expected results and symptoms, pain management, movement restrictions and the importance of exercise.
- Strengthening – Progressive strengthening of hip and thigh muscles is crucial to regain and promote function. In the early phase, strengthening begins with bed exercises, then progressing to standing and resistance training.
- Mobilization – Early mobilization (movement of the limbs and moving in bed) can be effective in reducing time in hospital, pain and reducing risk of blood clots.
- Gait Training – Weight bearing status and hip precautions must be taken into account when beginning to walk after a hip replacement. Early gait training typically involves a gait aid such as a walker, and can also include stair training.
- Equipment Recommendations – This can include gait aids such as walkers or rollators, raised toilet seat, grab bars, shower chairs and reachers.
Recovering From Hip Replacement Surgery
Recovery time for hip replacement surgery varies from person to person. Restrictions and recovery will also depend on the replacement approach. A full recovery may take from three months to one year. A gradual and slow to return to sports is best done through consultation with your therapist and surgeon.
Exercise has consistently been shown to improve patient outcomes after hip replacement surgery including clinical outcomes, pain levels and hospitalization.[viii] Our therapists can help provide the right guidance and intervention no matter the hip replacement rehabilitation stage. Whether suffering from hip pain, wanting to get stronger before surgery, needing the proper exercise routine after surgery or returning to sport, let us help you get back to doing what you love. We are one of Ontario’s leading centres for complex orthopedic injury rehabilitation.
Written by